Discover Tahiti: Your Ultimate Guide to Paradise
We will try to introduce you to Tahiti World Map through this blog. Let’s start by wondering what Tahiti can be an interesting place for. After reading our blog, you will understand why the Tahiti World Map is interesting. So let’s get started, Tahiti is located in the South Pacific Ocean, specifically in the region known as French Polynesia. It is part of the Society Islands archipelago, a group of islands that includes Tahiti and its neighboring islands such as Moorea. On the world map, Tahiti can be found southeast of Hawaii, northeast of New Zealand, and southwest of South America. It is located about halfway between Australia and South America. Tahiti’s coordinates are approximately 17.6509° S latitude and 149.4260° W longitude.
Introduction
Welcome to Tahiti World Map, the jewel of the South Pacific! With its breathtaking landscapes, vibrant culture, and warm hospitality, Tahiti is truly a paradise waiting to be explored. Whether you’re looking to relax on pristine beaches, adventure in lush jungles, or immerse yourself in rich Polynesian heritage, Tahiti offers something for every traveler. In this guide, we take you on a journey through Tahiti’s enchanting islands, offering insider tips, must-see attractions, and practical advice to ensure an unforgettable experience in this tropical haven. the epitome of heaven on earth. Located in the heart of the South Pacific, Tahiti is a destination that beckons tourists with its crystal-clear waters, lush greenery, and vibrant culture. In this comprehensive guide, we invite you to explore Tahiti’s awe-inspiring scenery, from its breathtaking landscape to its rich Polynesian heritage.
Location and Map Overview
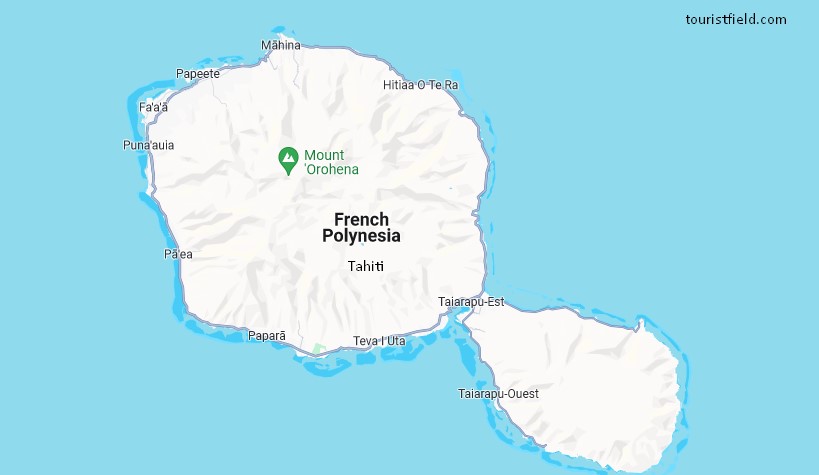
Tahiti World Map is the largest island of French Polynesia, an overseas territory of France located in the South Pacific Ocean. It is located in the archipelago of the Society Islands, which is part of a larger group of islands known as the Polynesian Triangle. Here is a brief description of its location and a general map:
Location:
- Tahiti is approximately 4,400 kilometers (2,700 miles) south of Hawaii.
- It lies about 7,900 kilometers (4,900 miles) from Australia.
- The island is roughly 6,200 kilometers (3,900 miles) northeast of New Zealand.
- Tahiti’s coordinates are approximately 17.6794° S latitude and 149.4068° W longitude.
Map Overview:
- Tahiti is shaped like a figure eight, with two main sections connected by a narrow isthmus.
- The larger section is Tahiti Nui (Big Tahiti) to the northwest, while the smaller section is Tahiti Iti (Small Tahiti) to the southeast.
- The island is surrounded by coral reefs and has a mountainous interior, with Mount Orohena being the highest peak at 2,241 meters (7,352 feet).
- The capital city, Papeete, is located on the northwest coast of Tahiti Nui and serves as the economic and political center of French Polynesia.
- The island is known for its stunning landscape, lush vegetation, and vibrant culture, which attracts tourists from all over the world.
This description provides a basic idea of Tahiti’s location and features. For more detailed maps and information, you can refer to geographic resources or online mapping services.
Islands of Tahiti
Major Islands:
- Tahiti: The largest and most populous island, with the capital city of Papeete and the main center of economic and political activity in French Polynesia.
- Moorea: Located just northwest of Tahiti, Moorea is known for its stunning scenery, including lush green fields, crystal-clear lagoons, and beautiful beaches. It is a popular destination for tourists looking for a more relaxed environment.
- Bora Bora: Famous for its luxury resorts, overwater bungalows, and breathtaking turquoise lagoon, Bora Bora is one of the world’s most iconic and romantic destinations.
- Huahine: Consisting of two main islands, Huahine Nui and Huahine Iti, this destination offers a blend of lush landscapes, archaeological sites, and traditional Polynesian culture.
- Raiatea and Tahaya: These sister islands are often referred to as a destination due to their proximity and shared lagoon. Raiatea is known as the “Sacred Island” and holds significant cultural and historical importance, while Taha’ is famous for its vanilla plantations and peaceful atmosphere.
Remote Islands:
- Marquesas Islands: Located northeast of Tahiti, the Marquesas Islands are characterized by their rugged beauty, dramatic landscapes, and rich cultural heritage. They are more remote and less visited than the main islands.
- Tuamotu Archipelago: This vast chain of atolls and low-lying islands is known for its stunning coral reefs, excellent diving opportunities, and secluded luxury resorts. Rangiroa and Fakarava are the most famous atolls of this group.
- Gambia Islands: Located southeast of Tahiti, the Gambia Islands are known for their historic sites, including the former capital of French Polynesia and a unique blend of Polynesian and European culture.
Austral Islands: Located south of Tahiti, the Austral Islands are known for their rugged beauty, pristine beaches, and vibrant marine life. Rurutu, Tubuai, and Raivai are some of the main islands in this group.
Terrain and Landscape
Volcanic Origin:
- Tahiti is of volcanic origin, formed from a series of volcanic eruptions millions of years ago.
- The island’s terrain is characterized by rugged mountains, deep valleys, and lush vegetation, shaped by volcanic activity.
- Although the island is no longer volcanically active, evidence of its volcanic past is still visible in its geology and geology.
Mountain Peak:
- Mount Orohena: Standing as the highest peak in French Polynesia, Mount Orohena reaches a height of 2,241 meters (7,352 ft). It is located in the central part of Tahiti and is a prominent feature of the island’s landscape.
- Mount Aorai: This mountain is Tahiti’s second-highest peak, with an elevation of 2,066 meters (6,778 ft). It is located northwest of Mount Orohena and offers stunning panoramic views of the island.
- Tahiti’s interior is characterized by a series of sharp mountains, deep valleys, and lush rainforests, formed by volcanic activity and erosion over millions of years.
Coastal Features:
- Tahiti has a diverse coastline, from sandy beaches to rugged cliffs and volcanic rock formations.
- The island is surrounded by coral reefs, especially along its lagoon-facing shores, which provide habitat for various marine life and contribute to the island’s stunning underwater scenery.
- Along the west and south coasts, you can find beautiful white sand beaches and calm, turquoise waters, making these areas popular for swimming, snorkeling, and water sports.
- Tahiti’s north and east coasts offer more rugged, rocky coastlines, dramatic cliffs, and choppy surf, offering stunning scenery and opportunities for coastal exploration.
Overall, Tahiti’s terrain and landscape display a dynamic interplay of volcanic power, erosion, and the influence of the surrounding ocean, creating a paradise for nature enthusiasts and explorers alike.
The beauty of Tahiti
Tahiti is renowned for its stunning natural beauty, characterized by green mountains, pristine beaches, and turquoise lagoons. One of the most iconic sights is Mount Otemanu, a majestic peak that towers over the island of Bora Bora. Visitors can start hiking to witness the scenic views of the surrounding landscapes or simply relax on the powdery white sands of Matira Beach.
Tahiti Agriculture
Agriculture plays an important role in the economy and culture of Tahiti and French Polynesia as a whole. Here is an overview of agriculture in Tahiti World Map:
Major crops:
- Vanilla: Tahiti is famous for its high-quality vanilla, prized for its rich flavor and aroma. Vanilla cultivation is an important industry on the island, with farmers carefully tending vanilla orchids to produce choice beans.
- Tropical Fruits: Tahiti’s tropical climate is conducive to growing a variety of fruits such as pineapples, mangoes, papayas, guavas, and citrus fruits. These fruits are not only consumed locally but also exported to other markets.
- Noni: Noni, a tropical fruit known for its medicinal properties, also grows in Tahiti. It is used in traditional Polynesian medicine and has gained popularity in the global wellness industry.
- Coffee: Although not as widespread as other crops, coffee cultivation is gaining traction in Tahiti, especially in the highlands where the environment is suitable for coffee plants.
Livestock and Fishing:
- Animal husbandry including cattle, pigs, and poultry is practiced in Tahiti to meet local demand for meat and dairy products.
- Fishing is an integral part of Tahitian culture and provides an important source of protein for the local population. Both subsistence and commercial fishing are practiced with a variety of fish and seafood caught in the surrounding waters.
Challenges and Opportunities:
- Limited arable land: Tahiti’s mountainous terrain limits the amount of arable land available for agriculture, leading to challenges in expanding agricultural production.
- Sustainable practices: There is growing interest in sustainable agricultural practices, including organic farming and agroforestry, to preserve the island’s fragile ecosystems and prevent soil erosion.
- Economic Diversification: Agriculture in Tahiti offers opportunities for economic diversification and rural development, particularly through value-added products such as specialty crops and agritourism experiences.
Overall, agriculture in Tahiti is characterized by a focus on high-value crops, traditional farming practices, and the need for sustainable development to ensure the sector’s long-term viability.
Explore Tahitian Culture
Beyond its natural splendor, Tahiti is home to a vibrant and diverse culture. Tahitians are known for their warm hospitality and rich traditions, which are deeply rooted in Polynesian history. Visitors can immerse themselves in local customs by participating in traditional dance performances, participating in coconut picking demonstrations, or learning about the art of making tapa cloth.
Adventure in Paradise
For adventure seekers, Tahiti offers countless thrilling experiences to satisfy every adrenaline craving. From snorkeling at Moorea’s coral gardens to shark-feeding trips at Rangiroa, there’s no shortage of excitement to be found in these pristine waters. For the ultimate adventure, consider embarking on a guided hike through the lush valleys of Tahiti Nui, where you’ll encounter hidden waterfalls and ancient archaeological sites.
Indulge in Tahitian cuisine
No trip to Tahiti would be complete without tasting the exquisite Tahitian cuisine. Influenced by a fusion of French, Polynesian, and Asian culinary traditions, Tahitian cuisine is a tantalizing mix of fresh seafood, tropical fruits, and aromatic spices. Be sure to sample local delicacies such as poisson crue (marinated raw fish), taro root puree, and freshly grilled mahi-mahi.
Plan your trip
When planning your trip to Tahiti, it is essential to consider factors such as climate, accommodation, and transportation. Tahiti enjoys a year-round tropical climate, with warm temperatures and occasional showers. For accommodation, there are a variety of options, from luxurious overwater bungalows to cozy beach villas. Transportation between the islands is primarily via domestic flights or inter-island ferries, providing convenient access to all corners of this tropical paradise.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Question: What is the best time to visit Tahiti World Map?
Answer: The best time to visit Tahiti World Map is during the dry season, which usually extends from May to October. During this period, you can expect sunny weather, minimal rainfall and comfortable temperatures, making it ideal for outdoor activities and beach holidays. - Question: Is a visa required to visit Tahiti?
Answer: Yes, visitors to Tahiti World Map must have a valid passport and obtain a tourist visa depending on their nationality. It is recommended to check the specific visa requirements and entry rules applicable in your country of residence before traveling. - Question: What are some places to visit in Tahiti?
Answer: Some of the must-see attractions in Tahiti include Bora Bora’s iconic Mount Otemanu, Moorea’s lush botanical gardens, and Papeete Cultural Center. Additionally, exploring pristine beaches, vibrant coral reefs, and natural waterfalls is highly recommended. - Question: What water sports can I enjoy in Tahiti?
Answer: Tahiti offers a plethora of water sports and recreational activities for all levels of enthusiasts. From snorkeling and diving among vibrant coral reefs to surfing legendary breaks and paddleboarding in tranquil lagoons, there’s no shortage of aquatic adventures to embark on. - Question: How can I get around the Tahiti World Map?
Answer: Getting around the Tahiti World Map is relatively easy, with various transportation options available to travelers. Renting a car or scooter offers the flexibility to explore the islands independently, while taxis, buses, and ferries provide convenient transportation between destinations. - Question: What is the currency used in Tahiti?
Answer: The official currency of Tahiti is the French Pacific Franc (XPF), abbreviated as CFP. Although credit cards are widely accepted in tourist areas and upscale establishments, it is recommended to carry some cash for transactions in local markets and small establishments.
Tahiti Future Outlook
The future outlook for agriculture in Tahiti holds both challenges and opportunities as the island experiences changing environmental, economic, and social factors. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Climate Change Resilience: Tahiti, like many other island states, is vulnerable to the effects of climate change, including rising temperatures, changing precipitation patterns, and more frequent extreme weather events. Agricultural practices must adapt to these changes by focusing on drought-resistant crops, improved water management, and sustainable land use practices.
- Technological innovation: The adoption of modern agricultural technologies, such as precision farming, hydroponics, and vertical farming, can help increase productivity and efficiency in Tahiti’s agricultural sector. In addition, advances in crop breeding and genetic engineering may lead to the development of new varieties better suited to the island’s unique climate and conditions.
Diversification and value-added products:
There is potential to expand the range of crops grown in Tahiti beyond traditional staples such as vanilla and tropical fruits. Investing in research and development to identify niche markets and value-added products such as organic products, specialty coffees and natural cosmetics derived from local plants can increase the competitiveness of Tahitian agriculture in domestic and international markets.
- Market access and trade: Improving infrastructure, transport networks, and market access is essential to connect local farmers to regional and global markets. Strengthening partnerships with neighboring countries and international trade partners can help diversify export opportunities and reduce dependence on imported food products.
- Sustainable Practices and Conservation: Due to Tahiti’s limited land area and fragile ecosystem, sustainable agricultural practices will be critical to conserving natural resources, protecting biodiversity, and reducing environmental degradation. These include promoting organic farming practices, agroforestry practices, and soil conservation practices to maintain soil fertility and prevent erosion.
- Community involvement and capacity building: Empowering local communities through education, training, and capacity-building initiatives can foster entrepreneurship, innovation, and resilience within the agricultural sector. Supporting the involvement of small-scale farmers, indigenous communities and youth in agriculture can contribute to sustainable rural development and food security in Tahiti.
By addressing these challenges and seizing opportunities for innovation and sustainable development, Tahiti can build a resilient and vibrant agricultural sector that contributes to the island’s economic prosperity, cultural heritage, and environmental stewardship for years to come.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Tahiti World Map is a destination, that offers tourists a perfect blend of natural beauty, cultural richness, and adventurous spirit. Whether you’re looking for relaxation on pristine beaches or the thrill of the great outdoors, Tahiti has something for everyone. So pack your bags, and embark on the journey of a lifetime to discover the magic of Tahiti.



Pingback: Where's Tahiti on a Map | The Largest Island in French Polynesia | Tourist Field